HOW METHOTREATE WORK?
HOW METHOTREXATE WORKS?
Developed over 70 years ago as an anti-folate chemotherapy agent, methotrexate (MTX) is a WHO ‘essential medicine’ that is now widely employed as a first-line treatment in auto-immune, inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis (RA), psoriasis, and Crone's disease. When used for these diseases patients typically take a once-weekly low-dose of MTX — a therapy that provides effective inflammatory control to tens of millions of people worldwide.
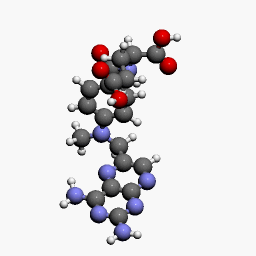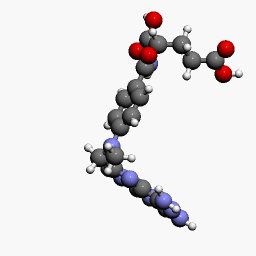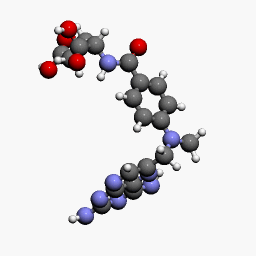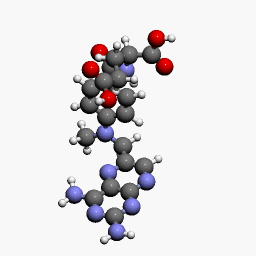
MTX is a methyl derivative of aminopterin and acts as an immunosuppressant. It is an analog of folic acid and inhibits dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR).
- DHFR is an essential enzyme for the synthesis of nucleotides. Folic acid from the diet is converted into dihydrofolate (DHF) and it is again converted into tetrahydrofolate (THF) by the enzyme DHFR. THF then converts into 5,10-methyl tetrahydrofolate (5,10 methyl THF); with the help of the enzyme thymidylate synthetase, the 5,10 methyl THF again forms the DHF.
- The enzyme thymidylate synthetase also converts Deoxyuridylate (dUMP) to dTMP (Dioxythymidylate). Then with the series of reactions, dTMP makes thiamine which is part of the nucleotide required for DNA synthesis.
- MTX is known to inhibit DHFR and thymidylate synthetase leading to decreased synthesis of thymine required for DNA synthesis. 5,10 methyl THF converts into 5-methyl THF by the enzyme methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR).
- 5,10 methyl THF recycled to THF by enzymatic reaction of methionine synthase, this reaction used Vitamine B12 as cofactor. The second reaction involves the conversion of homocysteine to methionine. MTX disturbs this cycle increases homocysteine and decreases methionine levels.
- MTX also inhibits 5- anino-imidazole-4-carboxamide ribonucleotide (AICAR)-transferase. This enzyme is essential for de novo purine synthesis i.e. it decreased the synthesis of adenine and guanine responsible for DNA and RNA synthesis.
- Impairment in nucleic acid synthesis suppresses the rapidly dividing cells such as immune cells and this essentially disrupts the S phase of the cell cycle responsible for making DNA.
|
It reduces the proliferation and immunoglobulin synthesis of peripheral lymphocytes by the reduction of polyamine synthesis. It also increased the level of adenosine, which pertains to the anti-inflammatory action of MTX. It changes the function of different immune cells such as decreased production of immunoglobulins, and inflammatory cytokines, reduced chemotaxis of polymorphonuclear cells, and inhibits NK and monocytes/, macrophages. |




Comments
Post a Comment